Description
Podiatry assistants help the podiatrist by carrying out supportive tasks such as assisting in diagnosing and treating the disorders, diseases, and deformities of the feet, advising people on foot care techniques, and the importance of foot care for promoting better mobility and general well-being. They also perform small tasks such as cutting toenails, applying plasters, and general clerical duties.
Duties
Podiatry assistants typically do the following:
- Patient Preparation: Prepare patients for examination and treatment, including taking medical histories, measuring vital signs, and preparing the necessary equipment.
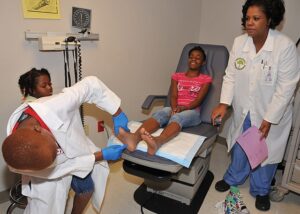
- Assisting with Procedures: Assist podiatrists during examinations and procedures by handling instruments, providing patient support, and maintaining a sterile environment.
- Wound Care: Clean and dress wounds, apply bandages, and provide instructions on wound care to patients.
- Orthotic Management: Assist in the fitting, adjustment, and maintenance of orthotic devices and other foot care products.
- Administrative Tasks: Schedule appointments, maintain patient records, handle billing and insurance claims, and perform other office management tasks.
- Patient Education: Educate patients on foot care practices, proper footwear, and exercises to maintain foot health.
- Equipment Sterilization: Clean, sterilize, and maintain medical instruments and equipment to ensure safety and hygiene standards are met.
- Inventory Management: Monitor and manage medical supplies and equipment inventory, ensuring that the clinic is well-stocked.
- Follow-up Care: Provide follow-up care instructions and support to patients, including post-procedure guidelines and rehabilitation exercises.
Other titles
The following job titles also refer to podiatry assistant:
assistant in chiropody
foot care assistant
assistant practitioner in podiatry
assistant in podiatry
chiropody assistant
podology assistant
assistant in podiatric foot care
podiatry foot care assistant
assistant in podology
Working conditions
Podiatry assistants work in various healthcare settings, including private podiatry clinics, hospitals, outpatient care centers, and nursing homes. The work environment is typically clean, well-lit, and equipped with specialized medical instruments and equipment. The role may require standing for extended periods, assisting with patient mobility, and handling potentially hazardous materials, such as sharp instruments and bodily fluids. Podiatry assistants must adhere to strict hygiene and safety protocols to prevent infections and ensure patient safety. Work hours are generally regular, but some positions may require evening or weekend shifts to accommodate patient schedules.
Minimum qualifications
To become a Podiatry Assistant, the following educational background and experience are typically required:
- Education: A high school diploma or equivalent is the minimum requirement. Post-secondary education, such as a certificate or diploma in medical assisting or a related field, is often preferred. Some programs offer specialized training in podiatric assisting.
- Certification: Certification as a medical assistant (CMA) or podiatric medical assistant (PMAC) can enhance job prospects and demonstrate professional competence. Certification requirements vary by region and certifying body.
- Training: On-the-job training is typically provided, covering specific podiatric procedures, use of medical equipment, and patient care techniques. Training programs may also be available through vocational schools, community colleges, or professional associations.
- Experience: Previous experience in a healthcare setting, such as working as a medical assistant, nursing assistant, or other allied health professional, is beneficial. Experience with administrative tasks and patient care can also be advantageous.
- Skills: Strong interpersonal and communication skills, attention to detail, empathy, and the ability to work well in a team are essential. Proficiency in basic medical procedures, knowledge of foot anatomy and common podiatric conditions, and familiarity with medical terminology and office software are also important.
Continuous professional development is encouraged to stay updated with advancements in podiatric care and medical assisting practices. Podiatry assistants may attend workshops, seminars, and continuing education courses to enhance their skills and knowledge. Membership in professional organizations, such as the American Society of Podiatric Medical Assistants (ASPMA), provides access to resources, networking opportunities, and further educational support.
ISCO skill level
ISCO skill level is defined as a function of the complexity and range of tasks and duties to be performed in an occupation. It is measured on a scale from 1 to 4, with 1 the lowest level and 4 the highest, by considering:
- the nature of the work performed in an occupation in relation to the characteristic tasks and duties
- the level of formal education required for competent performance of the tasks and duties involved and
- the amount of informal on-the-job training and/or previous experience in a related occupation required for competent performance of these tasks and duties.
Podiatry assistant is a Skill level 4 occupation.
Podiatry assistant career path
Similar occupations
These occupations, although different, require a lot of knowledge and skills similar to podiatry assistant.
podiatrist
homeopath
specialist pharmacist
acupuncturist
orthoptist
Essential knowledge and skills
Essential knowledge
This knowledge should be acquired through learning to fulfill the role of podiatry assistant.
- Dermatology: Dermatology is a medical specialty mentioned in the EU Directive 2005/36/EC.
- Orthopaedics: Orthopaedics is a medical specialty mentioned in the EU Directive 2005/36/EC.
- Chiropody: Medical practice dealing with disorders of the feet.
- Administrative tasks in a medical environment: The medical administrative tasks such as registration of patients, appointment systems, record keeping of patients information and repeated prescribing.
- Podiatric diseases: Field of information that distinguishes different kinds of podiatric diseases and disorders regarding foot problems, injuries and maladies, and how to treat them by using conservative and surgical options.
- Orthopaedic treatment alternatives: The appropriate available non-operative and operative treatment alternatives for common orthopaedic conditions and injuries, the benefits and limitations of each type of treatment as well as any potential side effects or complications of the treatment.
- Health records management: The procedures and importance of record keeping in a healthcare system such as hospitals or clinics, the information systems used to keep and process records and how to achieve maximum accuracy of records.
- Foot problems: Conditions and disorders affecting the health and well being of feet such as fungal infections, ingrown nails, verrucas, smelly feet, flat feet and bunions.
- Orthopaedic conditions: The physiology, pathophysiology, pathology, and natural history of common orthopaedic conditions and injuries.
- Types of orthopedic supplies: Various types of orthopaedic supplies such as braces and arm supports, used for physical therapy or physical rehabilitation.
- Clinical coding: The matching of clinical statements with standard codes of illnesses and treatments through use of a classification system.
- Podiatric surgery: The surgical specialty used to treat conditions and deformities of the feet such as tendon, heel and hammer toe surgery.
Essential skills and competences
These skills are necessary for the role of podiatry assistant.
- Respond to changing situations in health care: Cope with pressure and respond appropriately and in time to unexpected and rapidly changing situations in healthcare.
- Provide footwear advice to patients: Inform patients on the types of footwear available and suitable for their feet conditions or disorders to increase foot well being.
- Recommend orthotic devices: Suggest patients to use tailor-made insoles, padding and arch supports to relieve feet pain.
- Record treated patient’s information: Record information accurately relating to the progress of the patient during therapy sessions.
- Provide medication information: Provide patients with information about their medication, possible side effects, and contra-indications.
- Treat patients’ nails: Use a nail drill to reduce thickening toenails and remove debris from their sulci by inserting nail packs.
- Communicate effectively in healthcare: Communicate effectively with patients, families and other caregivers, health care professionals, and community partners.
- Promote foot health: Provide information and guidance on means to keep one’s feet healthy by wearing appropriate footwear or avoiding unhealthy practices such as fungal infections.
- Follow clinical guidelines: Follow agreed protocols and guidelines in support of healthcare practice which are provided by healthcare institutions, professional associations, or authorities and also scientific organisations.
- Advise on healthcare users’ informed consent: Ensure patients/clients are fully informed about the risks and benefits of proposed treatments so they can give informed consent, engaging patients/clients in the process of their care and treatment.
- Shape nails: Shape nails by cutting and smoothening the ends of the nails, with the use of files, scissors or emery boards.
- Comply with quality standards related to healthcare practice: Apply quality standards related to risk management, safety procedures, patients feedback, screening and medical devices in daily practice, as they are recognized by the national professional associations and authorities.
- Ensure safety of healthcare users: Make sure that healthcare users are being treated professionally, effectively and safe from harm, adapting techniques and procedures according to the person’s needs, abilities or the prevailing conditions.
- Collect healthcare user data under supervision: Collect qualitative and quantitative data related to the healthcare user’s physical, psychological, emotional and social status and functional ability within set parameters, monitoring healthcare user’s responses and status during the performance of assigned measures/tests and taking appropriate action, including reporting the findings to the physiotherapist.
- Develop a collaborative therapeutic relationship: Develop a mutually collaborative therapeutic relationship during treatment, fostering and gaining healthcare users’ trust and cooperation.
- Perform clinical coding procedures: Match and record correctly the specific illnesses and treatments of a patient by using a clinical codes classification system.
- Maintain medical devices: Ensure all medical devices and appliances are properly stored and taken care of so they maintain their functionality and appearance.
Optional knowledge and skills
Optional knowledge
This knowledge is sometimes, but not always, required for the role of podiatry assistant. However, mastering this knowledge allows you to have more opportunities for career development.
- Microbiology-bacteriology: Microbiology-Bacteriology is a medical specialty mentioned in the EU Directive 2005/36/EC.
- Medical terminology: The meaning of medical terms and abbreviations, of medical prescriptions and various medical specialties and when to use it correctly.
- Surgical asepsis: The way to keep equipment and surfaces sterile to prevent infections during medical care.
- Kinetics: The study of movement and its causes.
- Pharmacology: Pharmacology is a medical specialty mentioned in the EU Directive 2005/36/EC.
- Sterilization techniques: The methods and techniques used to destroy or remove microorganisms such as viruses and bacteria that can contaminate medical instruments or any type of material in a health care setting.
- Health care system: The structure and function of health care services.
- Human anatomy: The dynamic relationship of human structure and function and the muscosceletal, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, endocrine, urinary, reproductive, integumentary and nervous systems; normal and altered anatomy and physiology throughout the human lifespan.
Optional skills and competences
These skills and competences are sometimes, but not always, required for the role of podiatry assistant. However, mastering these skills and competences allows you to have more opportunities for career development.
- Contribute to quality physiotherapy services: Participate in activities that promote quality, particularly in the acquisition and evaluation of equipment, resources, safe storage and supply management.
- Place orders for orthopedic products: Order specialised orthopaedic materials and supplies for the store; maintain the company stock.
- Carry out wound care: Cleanse, irrigate, probe, debride, pack and dress wounds.
- Ensure proper appointment administration: Set up a proper procedure to manage appointments, including policies related to cancellation and nonappearance.
- Obtain healthcare user’s medical status information: Gather healthcare user information through various sources such as questioning the healthcare user, caregiver, or healthcare professional to obtain information on the patient`s health and social status, and interpreting records made by other health care professionals when appropriate.
- Analyse x-ray imagery: Analyse X-ray imagery in order to locate the sources of patients` difficulties and interpret the findings.
- Monitor stock level: Evaluate how much stock is used and determine what should be ordered.
- Treat nails: Wrap nails to repair them or make them stronger and more resilient. Soften, trim or push back nail cuticles and provide treatment to people who bite their nails.
- Provide health education: Provide evidence based strategies to promote healthy living, disease prevention and management.
- Monitor patient’s vital signs: Monitor and analyse vital signs of heart, respiration, and blood pressure.
- Process medical insurance claims: Contact the patient`s health insurance company and submit the appropriate forms with information on the patient and treatment.
- Conduct podiatry consultation: Asses the condition of the patient`s feet by cutting his/hers toenails, removing any hard skin and checking for corns, calluses or verrucas and decide on a diagnosis.
- Discuss the medical history of the healthcare user: Ask the healthcare user about his medical condition and physical well-being and the desired results to be achieved through the suggested therapy and follow the prescribed treatment.
- Recommend orthopedic goods to customers depending on their condition: Recommend and provide advice on orthopaedic goods and pieces of equipment such as braces, slings or elbow supports. Provide individual advice depending on customer’s specific condition and needs.
- Administer appointments: Accept, schedule and cancel appointments.
- Apply foot casts: Order, and cover patients’ legs, ankles and feet with foot casts and walking braces. These protect and support the lower leg and foot following fractures or injuries and reduce injury healing time.
- Send medical samples: Send samples containing accurate information to the medical laboratory for testing.
- Work in a multicultural environment in health care: Interact, relate and communicate with individuals from a variety of different cultures, when working in a healthcare environment.
- Employ foreign languages in care: Communicate in foreign languages with healthcare users, their carers, or services providers. Use foreign languages to faciliate patient care according to the needs of the patient.
- Work in multidisciplinary health teams: Participate in the delivery of multidisciplinary health care, and understand the rules and competences of other healthcare related professions.
- Apply wound dressings: Select and apply the appropriate wound dressings, such as liquid or spray occlusive materials, absorbent material or immobilising dressing, according to the surgical procedure undertaken.
Skills group distribution
ISCO group and title
2269 – Health professionals not elsewhere classifiedÂ
 References
- Podiatry assistant – ESCO
- Podiatry assistant | Explore careers – National Careers Service
- How Can I Become a Certified Podiatry Assistant? – Learn.org
- Featured image: By U.S. Navy photo by Mass Communications Specialist 2nd Class Riza Caparros – This image was released by the United States Navy with the ID 100811-N-8361C-002 (next).This tag does not indicate the copyright status of the attached work. A normal copyright tag is still required. Public Domain